Alhaji Aminu Wada Maida Appointed as the New Head of NCC
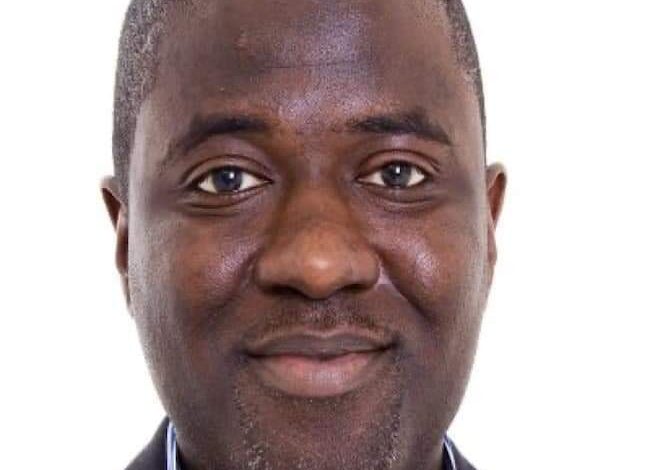

Alhaji Aminu Wada Maida Appointed as the New Head of NCC
Introduction
The Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) plays a vital role in regulating and promoting the telecommunications industry in Nigeria. Recently, a new chapter unfolded in the NCC’s history with the appointment of Alhaji Aminu Wada Maida as its new head. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of this appointment, Alhaji Maida’s background, and the potential impact on Nigeria’s telecommunications sector.

A New Leadership Era
Alhaji Aminu Wada Maida’s appointment as the head of the NCC marks a significant development in the country’s telecommunications landscape. The NCC, as the regulatory authority for the telecommunications industry in Nigeria, is responsible for ensuring the industry’s growth, innovation, and compliance with regulations.
Alhaji Maida’s Background
Alhaji Aminu Wada Maida brings a wealth of experience and expertise to his new role. Prior to this appointment, he served as the Executive Commissioner for Technical Services at the NCC, where he played a key role in shaping the regulatory framework for the telecommunications industry. He has a distinguished career that spans various sectors, and his leadership is expected to bring a fresh perspective to the NCC.
Key Areas of Impact
Alhaji Maida’s leadership is expected to influence several crucial areas in Nigeria’s telecommunications sector:
- Regulatory Framework: Alhaji Maida’s tenure may see a focus on fine-tuning and updating the regulatory framework to ensure it aligns with the rapidly evolving telecommunications landscape.
- Broadband Expansion: Expanding broadband access is a priority for Nigeria, and Alhaji Maida’s leadership may emphasize strategies to increase internet penetration, particularly in underserved areas.
- Innovation and Technology: The NCC under his guidance may encourage innovation and the adoption of emerging technologies, fostering an environment conducive to digital transformation.
- Consumer Protection: Ensuring that telecommunications consumers are protected, have access to affordable services, and are treated fairly by service providers could be a focus of Alhaji Maida’s leadership.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration with stakeholders, both domestic and international, to promote investment, growth, and standards compliance in the telecommunications sector.

Navigating the Digital Landscape: The Role of Regulatory Frameworks
In our increasingly interconnected world, where digital technologies and communication networks are the backbone of modern society, a well-crafted regulatory framework is essential. Regulatory frameworks serve as the rules and guidelines that govern various industries, ensuring they operate effectively, fairly, and in the best interest of consumers and the broader public. In this blog post, we’ll explore the significance of regulatory frameworks, their key components, and their pivotal role in shaping the digital landscape.
The Importance of Regulatory Frameworks
- Consumer Protection: Regulatory frameworks provide consumers with safeguards, ensuring that products and services meet safety and quality standards, and that consumers are treated fairly by service providers.
- Market Fairness: They promote competition and prevent monopolistic practices, fostering a fair market environment that encourages innovation and choice.
- Investor Confidence: Clear and consistent regulations instill confidence in investors and encourage capital flow into industries, supporting economic growth.
- Public Safety: In sectors like healthcare, transportation, and energy, regulatory frameworks are critical for ensuring public safety, setting standards, and enforcing compliance.
- Environmental Protection: Regulatory frameworks often include provisions for environmental sustainability, promoting responsible practices and reducing the impact on the environment.
Key Components of Regulatory Frameworks
- Laws and Regulations: The legal foundation of a regulatory framework is a set of laws and regulations that outline the rules and standards that businesses and organizations must follow.
- Oversight and Enforcement: Regulatory bodies and agencies are responsible for enforcing the regulations and ensuring compliance through inspections, investigations, and penalties for violations.
- Consumer Rights: Regulatory frameworks often include provisions for consumer protection, such as rights to information, privacy, and complaint resolution mechanisms.
- Transparency: Transparency is a fundamental principle, ensuring that regulations are clear, accessible, and understandable to all stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Effective regulatory frameworks involve stakeholders, including industry experts, consumers, and the public, in the development and review of regulations.
The Digital Landscape
In the digital age, regulatory frameworks have taken on a new level of significance, given the rapid pace of technological advancement and the far-reaching impact of the digital realm. Key areas of digital regulation include:
- Data Privacy: Regulations like the European Union’s GDPR and California’s CCPA aim to protect individuals’ data privacy, with provisions for consent, data access, and breach reporting.
- Cybersecurity: In an era of increasing cyber threats, regulations seek to establish security standards and breach notification requirements for businesses and organizations.
- Telecommunications: Regulations in the telecommunications sector ensure fair competition, protect consumer rights, and encourage the development of high-speed broadband networks.
- E-Commerce: Rules governing online commerce address issues such as electronic signatures, consumer protection, and cross-border transactions.
-
Emerging Technologies: The development of AI, blockchain, and IoT technologies introduces new regulatory challenges, from ethical guidelines to standards for data sharing.

Connecting the World: The Imperative of Broadband Expansion
In today’s digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, and access information. Yet, there are still many areas worldwide that lack adequate internet connectivity. Broadband expansion is the key to bridging this digital divide and ensuring that everyone has access to the opportunities and resources available online. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of broadband expansion, its impact on individuals and communities, and the challenges that need to be overcome.
The Significance of Broadband Expansion
- Equal Access: Broadband expansion aims to provide equal access to the internet for all, regardless of geographical location. It empowers individuals and communities to participate fully in the digital economy.
- Economic Growth: Access to broadband internet fosters economic growth by facilitating online commerce, attracting businesses, and creating jobs. It opens up opportunities for entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Education: Broadband access is crucial for students and educators. It supports online learning, enabling students to access educational resources and teachers to deliver remote instruction.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine and remote healthcare services rely on broadband connections to reach patients in underserved areas, improving healthcare access and outcomes.
- Social Inclusion: Broadband helps reduce social isolation by connecting people to their communities and providing access to social services, entertainment, and cultural resources.
- Emergency Response: Fast and reliable broadband connections are essential for emergency services, helping first responders coordinate efforts, share information, and save lives in times of crisis.
Impact on Individuals and Communities
- Economic Empowerment: Broadband expansion can empower individuals to create online businesses, find remote work opportunities, and access training and educational resources to enhance their employability.
- Improved Healthcare: Rural and underserved communities benefit from telemedicine services, ensuring they receive necessary medical care without long commutes.
- Education Opportunities: Students in remote areas can access quality educational materials and courses, reducing educational disparities.
- Community Development: Broadband connectivity can attract businesses, foster local entrepreneurship, and promote community development.
Challenges in Broadband Expansion
- Infrastructure Investment: Expanding broadband infrastructure, particularly in rural or underserved areas, requires substantial investment in network development and maintenance.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Regulatory challenges and bureaucracy can impede the deployment of broadband services.
- Affordability: Ensuring that broadband is affordable for all individuals and families, regardless of their financial situation, is a key challenge.
- Digital Literacy: Expanding access alone is not enough; digital literacy programs are needed to ensure individuals can make the most of the internet.
- Last-Mile Connectivity: Bridging the last-mile connectivity gap can be especially challenging in remote and sparsely populated areas.
Conclusion
The appointment of Alhaji Aminu Wada Maida as the head of the Nigerian Communications Commission is a significant development for the country’s telecommunications industry. It represents an opportunity to further enhance regulatory practices, drive innovation, and expand access to telecommunications services, particularly broadband, for all Nigerians. As Alhaji Maida takes the reins at the NCC, the industry and the nation as a whole will be watching with anticipation for the positive changes and developments that his leadership may bring.