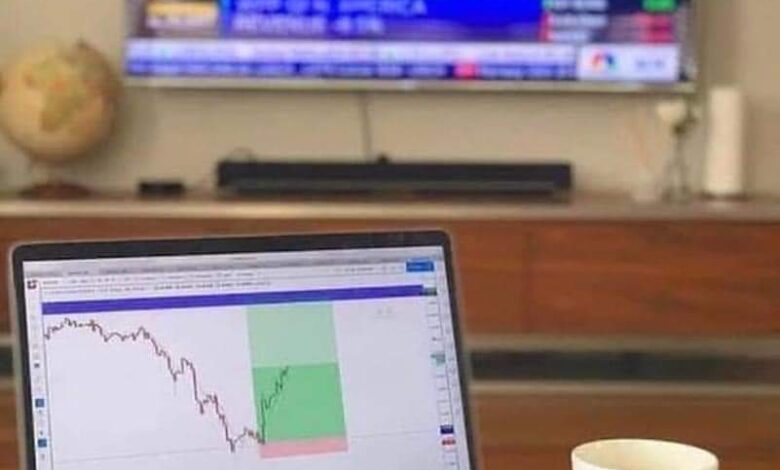
Deciphering Cryptocurrency Market Movement: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
The cryptocurrency market is a realm of high volatility and incredible opportunities. Understanding the dynamics behind cryptocurrency market movements is crucial for anyone looking to navigate this digital landscape successfully. In this blog post, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to interpret and comprehend cryptocurrency market movements. From the basics to advanced insights, we’ve got you covered.

Chapter 1: The Fundamentals
1.1. Cryptocurrency Basics – Understanding the core concepts of cryptocurrencies, including blockchain technology and digital assets.
1.2. Market Dynamics – Exploring the unique dynamics of cryptocurrency markets, such as 24/7 trading and global accessibility.
Chapter 2: Market Participants
2.1. Retail Traders – Insights into the role of individual traders in cryptocurrency markets and their impact on price movements.
2.2. Institutional Investors – Understanding how institutional investors influence market trends and liquidity.
Chapter 3: Market Indicators
3.1. Market Capitalization – Learn how market capitalization can provide insights into the relative size and importance of cryptocurrencies.
3.2. Trading Volume – Understand the significance of trading volume in assessing market liquidity and interest.
Chapter 4: Factors Affecting Cryptocurrency Prices
4.1. Supply and Demand – Examine how scarcity and demand for a cryptocurrency influence its value.
4.2. Market Sentiment – Delve into the role of news, social media, and community sentiment in driving price movements.
Chapter 5: Technical Analysis
5.1. Candlestick Charts – How to interpret candlestick charts to identify price patterns and trends.
5.2. Support and Resistance Levels – Understanding key price levels that can act as barriers or turning points.
5.3. Indicators and Oscillators – A detailed guide to using technical indicators like MACD, RSI, and moving averages for price analysis.
Chapter 6: Fundamental Analysis
6.1. Project Evaluation – Assessing the underlying technology, team, and real-world use cases of a cryptocurrency.
6.2. Market News and Events – Recognizing how significant news and events can drive market movements.
Chapter 7: Trend Analysis
7.1. Identifying Trends – How to recognize uptrends, downtrends, and sideways markets using various tools.
7.2. Trendlines and Patterns – Analyzing trendlines and chart patterns for predictive insights.
Chapter 8: Risk Management Strategies
8.1. Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders – Tools for managing risk and securing profits.
8.2. Position Sizing – Understanding how to adjust your investment size based on risk analysis.
Chapter 9: Staying Informed and Continuous Learning
9.1. News Sources and Tools – Discover reliable sources for cryptocurrency news and market data.
9.2. Educational Resources and Communities – Leveraging courses, forums, and communities to stay informed and improve your analysis skills.
Chapter 10: The Psychology of Trading
10.1. Emotional Discipline – The importance of controlling emotions and adhering to your analysis-based strategy.
10.2. Common Cognitive Biases – Identifying and mitigating biases that can impact trading decisions.
Chapter 11: Final Thoughts
Summarize the key takeaways from the guide and emphasize the need for continuous learning and practice in understanding cryptocurrency market movement.

Cryptocurrency Basics: Your Gateway to the Digital Financial Frontier
Cryptocurrencies have taken the world by storm, transforming the way we think about money, finance, and transactions. This blog post is your gateway to understanding the fundamental concepts and components of cryptocurrencies. Whether you’re new to this digital financial frontier or looking to reinforce your knowledge, read on to explore the essential cryptocurrency basics.
Chapter 1: What Are Cryptocurrencies?
1.1. Defining Cryptocurrencies – A clear explanation of what cryptocurrencies are and how they differ from traditional currencies.
1.2. The Birth of Bitcoin – A brief history of the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, and its impact on the financial world.
Chapter 2: How Do Cryptocurrencies Work?
2.1. Blockchain Technology – Exploring the underlying technology that powers cryptocurrencies, including the concept of the blockchain.
2.2. Decentralization – Understanding the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies and how it impacts security and transparency.
Chapter 3: Common Cryptocurrencies
3.1. Bitcoin (BTC) – An in-depth look at the pioneering cryptocurrency, its features, and its uses.
3.2. Ethereum (ETH) – An introduction to Ethereum, known for its smart contract capabilities and decentralized applications.
3.3. Altcoins – Exploring other cryptocurrencies beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum and their unique features.
Chapter 4: Wallets and Addresses
4.1. Cryptocurrency Wallets – An overview of the different types of cryptocurrency wallets, including software, hardware, and paper wallets.
4.2. Public and Private Keys – Understanding the concept of public and private keys and their role in securing your assets.
Chapter 5: How to Buy and Sell Cryptocurrencies
5.1. Cryptocurrency Exchanges – Exploring the various types of exchanges and how to choose the right one for your needs.
5.2. Buying Cryptocurrencies – A step-by-step guide on how to purchase cryptocurrencies with traditional currency.
5.3. Selling Cryptocurrencies – The process of selling your digital assets and converting them into traditional currency.
Chapter 6: Security and Safety
6.1. Cryptocurrency Security – Tips on how to secure your cryptocurrencies, including the use of strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
6.2. Avoiding Scams and Frauds – Guidance on identifying and avoiding common cryptocurrency scams and fraudulent schemes.
Chapter 7: Using Cryptocurrencies
7.1. Online and Offline Transactions – Exploring how to use cryptocurrencies for online purchases and in physical stores.
7.2. International Transfers – The advantages of cryptocurrencies for cross-border payments and remittances.
Chapter 8: Price Volatility and Risk
8.1. Price Fluctuations – Understanding the inherent volatility of cryptocurrency prices and the factors that drive it.
8.2. Risk Management – Strategies for managing risk in cryptocurrency investments.
Chapter 9: Legal and Regulatory Considerations
9.1. Global Regulatory Landscape – An overview of cryptocurrency regulations and their impact on users.
9.2. Tax Implications – Exploring the tax considerations associated with owning and trading cryptocurrencies.
Chapter 10: The Future of Cryptocurrencies
10.1. Innovations and Developments – A glimpse into the exciting developments and innovations in the cryptocurrency space.
10.2. Challenges and Opportunities – An overview of the challenges cryptocurrencies face and the potential opportunities they offer.
Unveiling Market Dynamics: Understanding the Forces that Shape Financial Markets
Market dynamics is the heartbeat of financial markets. It encompasses the interplay of various factors, both internal and external, that influence price movements and trading activities. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of market dynamics, shedding light on the fundamental concepts, key forces, and how they collectively shape financial markets.
Chapter 1: Market Participants
1.1. Retail Traders – Exploring the role of individual investors and their impact on market dynamics.
1.2. Institutional Investors – Understanding the influence of large entities such as mutual funds, hedge funds, and pension funds.
Chapter 2: Supply and Demand
2.1. Price and Quantity – A look at the basic economic principles of supply and demand and how they impact market dynamics.
2.2. Market Orders – Understanding how market orders, limit orders, and stop orders affect order flow.
Chapter 3: Market Sentiment
3.1. Psychology of Trading – Analyzing how traders’ emotions and sentiment can drive market movements.
3.2. News and Social Media – Exploring the role of news, social media, and rumors in shaping market sentiment.
Chapter 4: Market Indicators
4.1. Market Capitalization – An overview of market capitalization as a measure of the size and importance of a market or asset.
4.2. Trading Volume – Understanding the significance of trading volume and its implications for liquidity.
Chapter 5: Economic Factors
5.1. Macroeconomic Indicators – Examining the impact of economic indicators such as GDP, inflation, and interest rates on market dynamics.
5.2. Microeconomic Factors – Understanding how individual company performance and industry trends influence markets.
Chapter 6: Market Trends and Patterns
6.1. Identifying Trends – Learning how to recognize trends, including uptrends, downtrends, and sideways markets.
6.2. Chart Patterns – Analyzing chart patterns like head and shoulders, flags, and pennants.
Chapter 7: Global Events and Geopolitics
7.1. International Events – Exploring how global events, including geopolitical tensions and economic crises, can trigger market movements.
7.2. Interconnected Markets – Understanding the interconnectedness of global markets and how one market’s dynamics can impact others.
Chapter 8: Technology and High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
8.1. Technological Advances – The impact of technology, algorithmic trading, and high-frequency trading on market dynamics.
8.2. Market Manipulation – Discussing the challenges and risks of market manipulation in the age of high-frequency trading.
Chapter 9: Regulation and Market Oversight
9.1. Regulatory Bodies – An overview of regulatory agencies and their role in maintaining fair and orderly markets.
9.2. Market Surveillance – How exchanges and regulatory bodies monitor and investigate market activities.
Chapter 10: Market Volatility and Risk Management
10.1. Understanding Volatility – Examining the nature of market volatility and its implications for traders and investors.
10.2. Risk Mitigation – Strategies for managing risk, including diversification, hedging, and stop-loss orders.
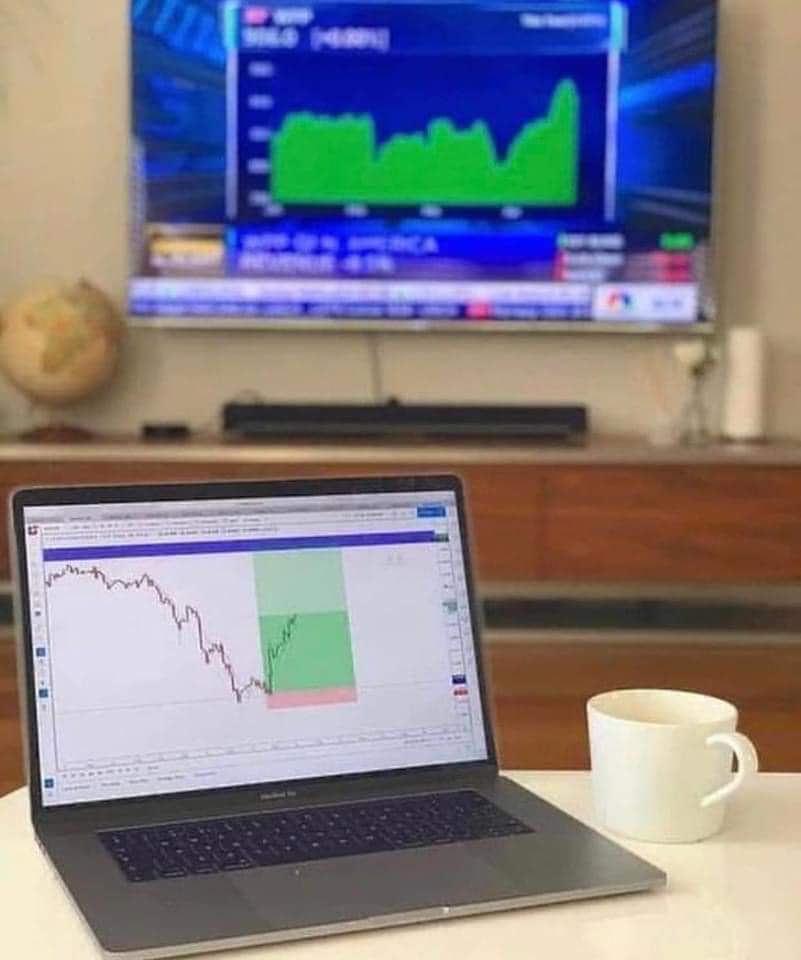
Chapter 11: Final Thoughts
Summarize the key takeaways from the guide and emphasize the importance of staying informed, practicing risk management, and continually adapting to changing market dynamics.
Conclusion:
Mastering cryptocurrency market movement analysis is an ongoing process that requires dedication and discipline. While it doesn’t guarantee success, a solid understanding of market dynamics, combined with technical and fundamental analysis, can significantly enhance your ability to make informed trading and investment decisions in the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies. Happy trading and analyzing!









The more apps that accept the token, the higher the Dogecoin price goes as a result. In fact, the Dogecoin price has claimed a lot in its recent history, and it has fallen, making it volatile. Unlike Bitcoin, it is easier to mine, and unlike Bitcoin, its followers are a lot more enthusiastic about it and accept it. Dogecoin’s implementation differs from its predecessors: It was originally forked from Litecoin, then refactored to Bitcoin. Dogecoin’s target block time is 1 minute, as opposed to Litecoin’s 2.5 minutes and Bitcoin’s 10 minutes. Mining is a way to earn your own cryptocurrency, and this guide will teach you exactly how to do it. You can establish ownership of Dogecoin with a private key, a code similar to a password that allows you to access a cryptocurrency. These keys are often held in crypto wallets.
https://www.bokkmarking-signs.win/earn-crypto
According to Tether’s website tether can be newly issued, by purchase for dollars, or redeemed by exchanges and qualified corporate customers excluding U.S.-based customers. Journalist Jon Evans states that he has not been able to find publicly verifiable examples of a purchase of newly issued tether or a redemption in the year ending August 2018. article h2:first-childarticle > div > p:first-childTether was founded as a start-up in 2014 in Santa Monica, California by entrepreneurs Brock Pierce, Reeve Collins, and Craig Sellars. The crypto world needs a stable coin. Crypto traders need a stable coin to park their wealth. Cross border crypto transfers need a stable coin to ensure correct value transfer. Regular people could also benefit from a stable coin (especially people living in countries such as Venezuela where their fiat currency is itself imploding.) In truth, everyone in blockchain, from beginners to experts, would greatly benefit from stable coins — when they prove to be one of the catalysts for mass adoption.